When it comes to choosing the right wheels for your vehicle, one of the key questions is whether the OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) wheels are cast or forged. Both casting and forging are common manufacturing processes, but they produce wheels with different characteristics. In this article, we’ll explore the differences between cast and forged OEM wheels, as well as how OEM investment casting plays a crucial role in producing high-quality wheels and other products, such as OEM cast steel gate valves and OEM casting PU gel insole resins.
What is OEM Investment Casting?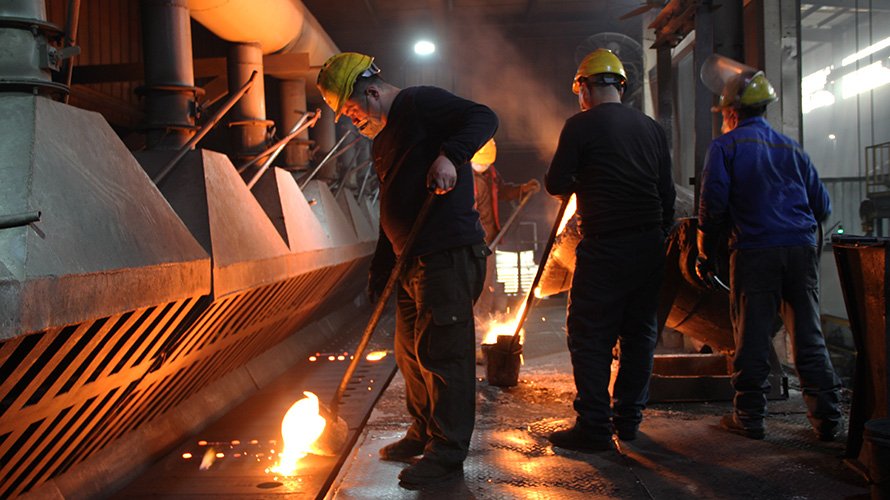
OEM investment casting is a precise manufacturing process that involves creating a wax model of the product, which is then coated in a ceramic shell. The shell is heated to remove the wax, and molten metal is poured into the mold. This technique is ideal for producing complex shapes and is used in a variety of industries, including automotive and industrial equipment manufacturing. Investment casting is especially beneficial for producing high-strength, durable components like OEM cast steel gate valves and other precision-engineered parts.
Cast vs. Forged Wheels: What's the Difference?
OEM Cast Wheels:
Cast wheels are produced by pouring molten metal (such as aluminum) into a mold and allowing it to cool and solidify into the shape of the wheel. This process is less expensive and quicker than forging, making it a common choice for OEM manufacturers. Cast wheels, including OEM wheels, are typically more affordable and are found in many standard vehicles. However, they may not offer the same level of strength and weight-saving advantages as forged wheels.
Advantages of Cast Wheels:
Lower cost
Easier to mass-produce
Good for standard vehicles
More variety in design and style
Disadvantages of Cast Wheels:
Lower strength compared to forged wheels
Potential for less durability under extreme conditions
Heavier than forged wheels
OEM Forged Wheels:
Forged wheels are made by applying intense heat and pressure to a solid billet of metal. This process aligns the metal's grain structure, creating a stronger, more durable product. Forged wheels are typically used in high-performance and luxury vehicles where strength, weight savings, and aesthetics are crucial.
Advantages of Forged Wheels:
Greater strength and durability
Lighter weight, which improves performance
Better resistance to cracking and deformation
More efficient for high-performance vehicles
Disadvantages of Forged Wheels:
Higher cost due to more complex manufacturing
Longer production time
Typically used in premium vehicles
Why OEM Manufacturers Choose Casting or Forging
The choice between cast or forged wheels depends largely on the intended use of the vehicle. OEMs consider factors like vehicle performance, cost, and manufacturing time when making this decision.
For example, OEM cast steel gate valves, which are used in industrial applications, often require the investment casting process to ensure precision and durability. Similarly, in automotive applications, the OEM casting process allows manufacturers to create lightweight and aesthetically pleasing wheels while maintaining cost-effectiveness for standard models.
On the other hand, forged wheels are more commonly found on vehicles requiring enhanced performance, such as sports cars or high-end luxury vehicles. The ability to produce lighter, stronger wheels with reduced weight makes forged wheels ideal for enhancing a vehicle's performance and fuel efficiency.
OEM Casting in Other Industries
OEM casting isn’t limited to automotive wheels. It's also essential in manufacturing a wide range of products across various industries. Take OEM casting PU gel insole resin, for example. The casting process allows manufacturers to produce ergonomic insoles that are both comfortable and durable. These insoles are often made with PU gel resins, which provide cushioning and shock absorption for added comfort.
In the valve industry, OEM cast steel gate valves are essential components that regulate the flow of liquids and gases in pipelines. The casting process ensures that these valves are durable and can withstand high pressure and extreme temperatures, making them ideal for industrial applications.
Conclusion: Cast or Forged—Which is Right for You?
When it comes to OEM wheels, whether cast or forged, the choice depends on your priorities. Cast wheels are affordable, easy to produce, and perfect for standard vehicles, while forged wheels are stronger, lighter, and more suitable for high-performance applications. Both processes play crucial roles in the automotive industry and beyond, with OEM investment casting offering a versatile and precise solution for many types of products, including cast steel gate valves and specialized PU gel insoles.
If you're considering upgrading your vehicle’s wheels, understanding the difference between casting and forging can help you make an informed decision. Whether you opt for the cost-effective solution of OEM cast wheels or the premium strength of forged wheels, both options are integral to the automotive and industrial sectors, providing reliable and durable performance.






